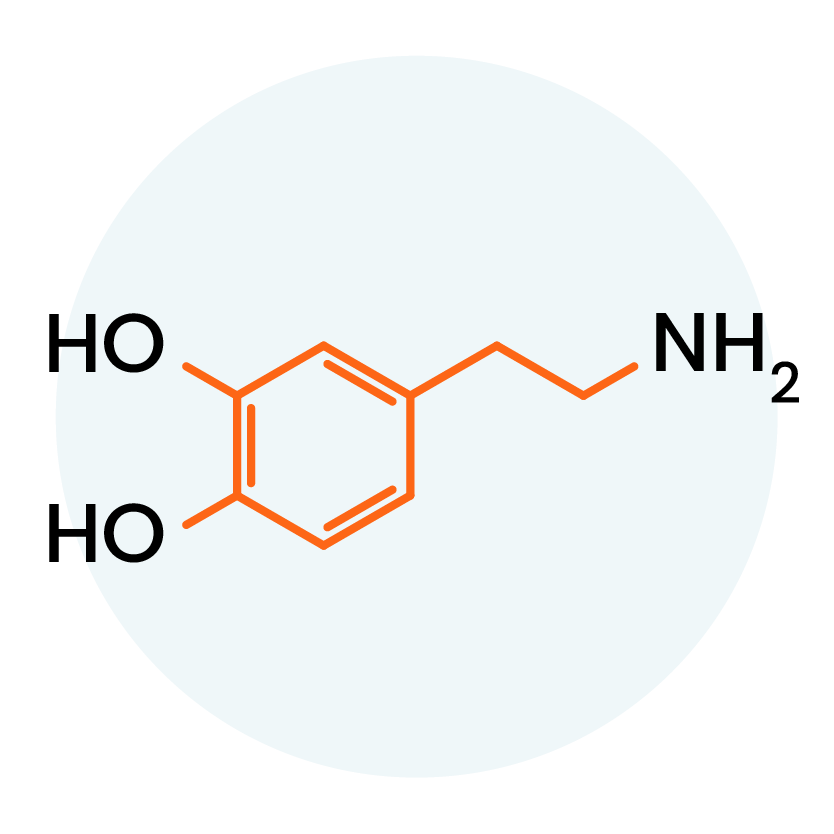
Dopamine
Dopamine is the “feel-good” neurotransmitter. It is associated with pleasure, motivation, and heightened arousal. It also helps with memory, concentration, sleep, and mood.
However, deviations from this balance, whether in the form of insufficient or excessive dopamine levels, can significantly impact mental health. Imbalances in dopamine levels may cause addiction, depression, and schizophrenia.