Reverse Osmosis Water Systems
Water purity directly affects the efficacy, reliability, and success of laboratory work. Different workflows and applications may require different levels of purity, but clean, clear water affects all laboratory processes from cleaning glassware to preparation of reagents and sampling. Reverse osmosis systems provide one of the most efficient systems for creating purified water.
This type of system can remove minerals, bacteria, and other harmful pathogens, helping your lab to function with the highest-quality feed water. The following list contains several benefits and considerations for choosing the best reverse osmosis water system.

Reverse osmosis is economical.
Reverse Osmosis is the most economical method to remove up to 99% of your water's impurities. The RO membrane is semi-permeable with a thin microporous surface that rejects virtually all dissolved materials, including dissolved inorganic solids, organics, particles, and microorganisms.
RO water is versatile.
RO water can be used to prepare microbiological buffers and chemical reagents. Additionally, it is a great option for use in general laboratory equipment, such as water baths, humidifiers, and autoclaves. RO water is also an excellent pretreatment choice for our Type I systems.
Reverse osmosis removes up to 99% of feed water contaminants.
As the feed water approaches the RO membrane, impurities deposit on the surface of the RO membrane and are flushed away to the drain. The purified product water that passes through the membrane is cleared of up to 99% of its impurities. The specific rejection rates of all the impurities are shown in each of the product specifications.
Osmotic Flow of Water
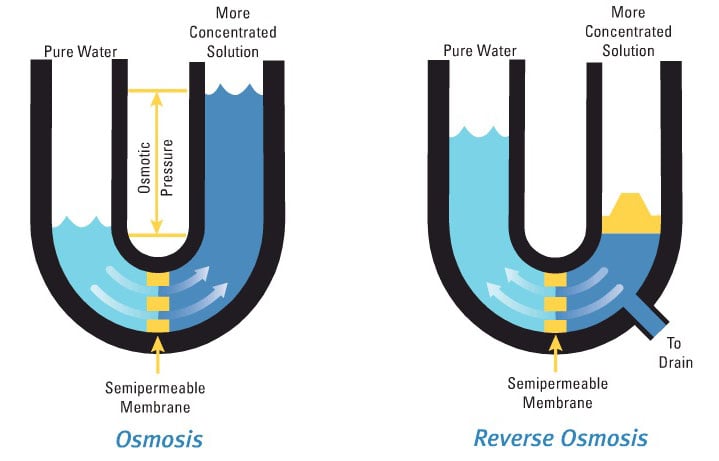
The figure above illustrates the natural osmotic flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane from less concentrated solutions to more concentrated solutions. Reverse osmosis is achieved if an external pressure is applied to reverse this natural flow, as shown on the right.
Feed Water Factors
Certain characteristics of your feed water directly relate not only to membrane performance and lifetime but also directly impact the quality of your product water.
Temperature
The volumes listed for the reverse osmosis product water are based on a feed water temperature of 25°C (77°F). For every 1°C below 25°C (77°F), the quantity of product water is reduced by 3%. Additionally, if the feed water temperature goes beyond 35°C (95°F), the RO membrane may be damaged. Thermo Scientific recommends a hot and cold water mixing valve to regulate the temperature to 25°C (77°F).
Alkalinity and Calcium
Carbonates, bi-carbonates, hydroxides and calcium impurities in your feed water contribute to scaling on an RO membrane. The Membrane Protection System (MPS) system is standard in our Barnstead RO systems to protect the RO membrane against such impurities, however, if the levels are high enough, our Pure Water Experts can recommend alternative technologies to prolong the life of your membrane and keep your system running efficiently.
Chlorine
Chlorine can damage the RO membrane and reduce its performance and life. Our Pure Water Experts can recommend the appropriate activated carbon cartridge to protect your RO system.
Turbidity
The turbidity level indicates the amount of suspended solids present. This suspended material can shorten the life of filters and reverse osmosis membranes if not properly treated. Our Pure Water Experts can recommend pretreatment options if this is an issue with your feed water.


